
Urea N46% is a white crystalline solid fertilizer widely recognized for its high nitrogen (N) content—46% by weight, making it the most concentrated solid nitrogen fertilizer available on the market. Renowned for its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and versatility, it plays a crucial role in modern agriculture and industrial processes across the globe. Its ability to enhance soil fertility and significantly improve crop yield has made Urea N46% a staple in farming communities worldwide.
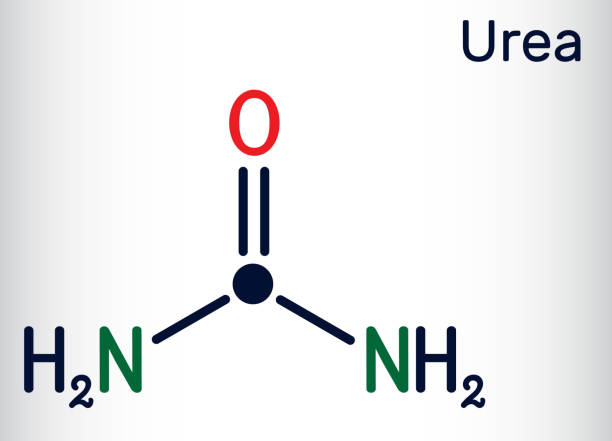
Urea N46%, also known as Carbamide, is an organic compound with the chemical formula CO(NH₂)₂, consisting mainly of nitrogen and carbon-based molecules. It features a free-flowing, non-clotted structure, treated with anti-caking agents to prevent lump formation during storage or transportation, even in high humidity.
Key characteristics include:
100% free from impurities, sand, and dust
Certified non-radioactive
pH range: 8.0 – 8.5 (slightly alkaline)
High water solubility, ideal for moist soil application or fertigation
Urea N46% is primarily available in two forms:
Granular Urea: Larger and more durable, ideal for mechanical spreaders and bulk blending.
Prilled Urea: Smaller particles, offering faster dissolution and suited for precision applications.
Though physically different, both forms provide identical nitrogen content and performance in the field.
Over 90% of Urea N46% production is used in agriculture as a nitrogen-release fertilizer, with a nutrient grade of 46–0–0 (46% N, 0% P, 0% K). It is especially favored for nitrogen-intensive crops such as:
Corn (maize)
Wheat
Rice
Sugarcane
Its high nitrogen concentration reduces transportation and application costs, making it ideal for both small-scale and commercial farming.
Urea N46% is typically applied at rates between 40 to 300 kg/ha, depending on soil fertility, crop type, and yield goals.
Best practices include:
Apply before or during rainfall to reduce nitrogen volatilization
Incorporate into soil mechanically or irrigate immediately after surface application
Ensure even distribution for consistent crop development
Avoid over-application, which may cause nitrogen leaching or runoff
For maximum efficiency, Urea should be applied based on soil tests, seasonal conditions, and specific crop needs.

While highly effective, Urea N46% can pose environmental risks if misused:
Volatilization: Nitrogen loss as ammonia gas if left on the soil surface
Leaching: Movement of nitrogen into groundwater, causing contamination
To mitigate these issues:
Use urease inhibitors or stabilizers
Split applications across the growing season
Combine with precision agriculture tools and soil moisture management
In addition to agriculture, Urea N46% is vital in various industries:
Melamine production (used in plastics and laminates)
Urea-formaldehyde resins (for adhesives and coatings)
Nitrogen-rich chemical reagents
Note: Fertilizer-grade Urea is not suitable for food or pharmaceutical uses.
Urea N46% supports sustainable farming when applied responsibly:
Reduces number of applications, saving fuel and labor
Optimizes yield with less input
Supports innovations such as controlled-release formulations and coated fertilizers
These advancements aim to make Urea N46% both eco-friendly and economically viable.
1. Biuret Toxicity:
Urea may contain biuret, an impurity harmful to plant growth.
Acceptable biuret levels are below 1.5% in fertilizer-grade Urea.
2. Nitrogen Loss:
Caused by volatilization or leaching.
Solutions include timely application, soil incorporation, or use of additives.
For best results:
Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
Keep bags or bulk containers sealed and off the ground
Avoid long-term exposure to humidity, as Urea is hygroscopic
With proper storage, Urea N46% retains its quality and shelf life for extended periods.